Chapter 6H. Typical Applications
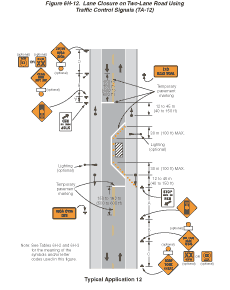
Notes for Figure 6H-12—Typical Application 12
Lane Closure on Two-Lane Road Using Traffic Control Signals
Standard:
- TTC signals shall be installed and operated in accordance with the provisions of Part 4. TTC signals shall meet the physical display and operational requirements of conventional traffic control signals.
- TTC signal timing shall be established by authorized officials. Durations of red clearance intervals shall be adequate to clear the one-lane section of conflicting vehicles.
- When the TTC signal is changed to the flashing mode, either manually or automatically, red signal indications shall be flashed to both approaches.
- Stop lines shall be installed with TTC signals for intermediate and long-term closures. Existing conflicting pavement markings and raised pavement marker reflectors between the activity area and the stop line shall be removed. After the TTC signal is removed, the stop lines and other temporary pavement markings shall be removed and the permanent pavement markings restored.
- Safeguards shall be incorporated to avoid the possibility of conflicting signal indications at each end of the TTC zone.
Guidance:
- Where no-passing lines are not already in place, they should be added.
- Adjustments in the location of the advance warning signs should be made as needed to accommodate the horizontal or vertical alignment of the roadway, recognizing that the distances shown for sign spacings are minimums. Adjustments in the height of the signal heads should be made as needed to conform to the vertical alignment.
Option:
- Flashing warning lights shown on the ROAD WORK AHEAD and the ONE LANE ROAD AHEAD signs may be used.
- Removable pavement markings may be used.
Support:
- TTC signals are preferable to flaggers for long-term projects and other activities that would require flagging at night.
- The maximum length of activity area for one-way operation under TTC signal control is determined by the capacity required to handle the peak demand.
Figure 6H-12 Lane Closure on Two-Lane Road Using Traffic Control Signals (TA-12)
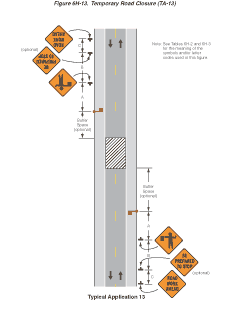
Notes for Figure 6H-13—Typical Application 13
Temporary Road Closure
Support:
- Conditions represented are a planned closure not exceeding 20 minutes during the daytime.
Standard:
- A flagger or uniformed law enforcement officer shall be used for this application. The flagger, if used for this application, shall follow the procedures noted in Sections 6E.04 and 6E.05.
Guidance:
- The uniformed law enforcement officer, if used for this application, should follow the procedures noted in Sections 6E.04 and 6E.05.
Option:
- A BE PREPARED TO STOP sign may be added to the sign series.
Guidance:
- When used, the BE PREPARED TO STOP sign should be located before the Flagger symbol sign.
Figure 6H-13 Temporary Road Closure (TA-13)
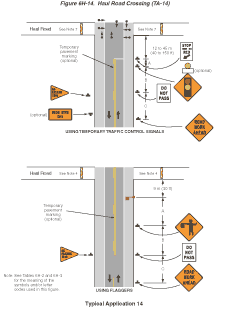
Notes for Figure 6H-14—Typical Application 14
Haul Road Crossing
Guidance:
- Floodlights should be used to illuminate haul road crossings where existing light is inadequate.
- Where no passing lines are not already in place, they should be added.
Standard:
- The traffic control method selected shall be used in both directions.
Flagging Method
- When a road used exclusively as a haul road is not in use, the haul road shall be closed with Type III barricades and the Flagger symbol signs covered.
- The flagger shall follow the procedures noted in Sections 6E.04 and 6E.05.
- At night, flagger stations shall be illuminated, except in emergencies.
Signalized Method
- When a road used exclusively as a haul road is not in use, Type III barricades shall be in place. The signals shall either flash yellow on the main road or be covered, and the Signal Ahead and STOP HERE ON RED signs shall be covered or hidden from view.
- The TTC signals shall control both the highway and the haul road and shall meet the physical display and operational requirements of conventional traffic control signals as described in Part 4. Traffic control signal timing shall be established by authorized officials.
- Stop lines shall be used on existing highway with TTC signals.
- Existing conflicting pavements markings between the stop lines shall be removed. After the TTC signal is removed, the stop lines and other temporary pavement markings shall be removed and the permanent pavement markings restored.
Figure 6H-14 Haul Road Crossing (TA-14)
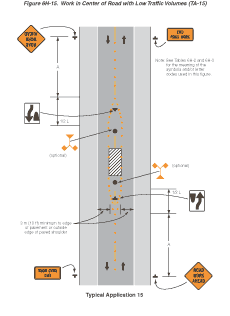
Notes for Figure 6H-15—Typical Application 15
Work in Center of Road with Low Traffic Volumes
Guidance:
- The lanes on either side of the center work space should have a minimum width of 3 m (10 ft) as measured from the near edge of the channelizing devices to the edge of pavement or the outside edge of paved shoulder.
- Workers in the roadway should wear high-visibility safety apparel as described in Section 6D.03.
Option:
- Flashing warning lights and/or flags may be used to call attention to the advance warning signs.
- If the closure continues overnight, warning lights may be used on the channelizing devices.
- A lane width of 2.7 m (9 ft) may be used for short-term stationary work on low-volume, low-speed roadways when motor vehicle traffic does not include longer and wider heavy commercial vehicles.
- A work vehicle displaying high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights may be used instead of the channelizing devices forming the tapers or the high-level warning devices.
- Vehicle hazard warning signals may be used to supplement high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights.
Standard:
- Vehicle hazard warning signals shall not be used instead of the vehicle’s high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights.
Figure 6H-15 Work in Center of Road with Low Traffic Volumes (TA-15)
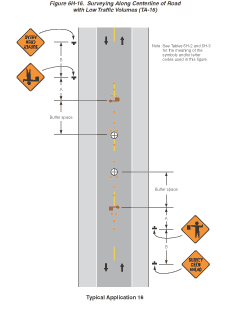
Notes for Figure 6H-16—Typical Application 16
Surveying Along Centerline of Road with Low Traffic Volumes
Guidance:
- Cones should be placed 150 mm (6 in) to 300 mm (12 in) on either side of the centerline.
- When using metric units, spacing of channelizing devices should not exceed a distance in meters equal to 1/5 of the speed limit (km/h) when used for taper channelization and a distance in meters equal to 2/5 of the speed limit (km/h) when used for tangent channelization. When using English units, spacing of channelizing devices should not exceed a distance in feet equal to the speed limit (mph) when used for the taper channelization and a distance in feet of 2 times the speed limit (mph) when used for tangent channelization.
- A flagger should be used to warn workers who cannot watch road users.
- Workers in the roadway should wear high-visibility safety apparel as described in Section 6D.03.
Standard:
- For surveying on the centerline of a high-volume road, one lane shall be closed using the information illustrated in Figure 6H-10.
Option:
- A high-level warning device may be used to protect a surveying device, such as a target on a tripod.
- Cones may be omitted for a cross-section survey.
- ROAD WORK AHEAD signs may be used in place of the SURVEY CREW AHEAD signs.
- Flags may be used to call attention to the advance warning signs.
- If the work is along the shoulder, the flagger may be omitted.
- For a survey along the edge of the road or along the shoulder, cones may be placed along the edge line.
- A BE PREPARED TO STOP sign may be added to the sign series.
Guidance:
- When used, the BE PREPARED TO STOP sign should be located before the Flagger symbol sign.
Figure 6H-16 Surveying Along Centerline of Road with Low Traffic Volumes (TA-16)
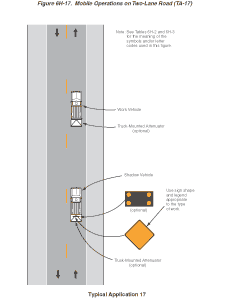
Notes for Figure 6H-17—Typical Application 17
Mobile Operations on Two-Lane Road
Standard:
- Vehicle-mounted signs shall be mounted in a manner such that they are not obscured by equipment or supplies. Sign legends on vehicle-mounted signs shall be covered or turned from view when work is not in progress.
- Shadow and work vehicles shall display high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights.
- If an arrow panel is used, it shall be used in the caution mode.
Guidance:
- Where practical and when needed, the work and shadow vehicles should pull over periodically to allow vehicular traffic to pass.
- Whenever adequate stopping sight distance exists to the rear, the shadow vehicle should maintain the minimum distance from the work vehicle and proceed at the same speed. The shadow vehicle should slow down in advance of vertical or horizontal curves that restrict sight distance.
- The shadow vehicles should also be equipped with two high-intensity flashing lights mounted on the rear, adjacent to the sign.
Option:
- The distance between the work and shadow vehicles may vary according to terrain, paint drying time, and other factors.
- Additional shadow vehicles to warn and reduce the speed of oncoming or opposing vehicular traffic may be used. Law enforcement vehicles may be used for this purpose.
- A truck-mounted attenuator may be used on the shadow vehicle or on the work vehicle.
- If the work and shadow vehicles cannot pull over to allow vehicular traffic to pass frequently, a DO NOT PASS sign may be placed on the rear of the vehicle blocking the lane.
Support:
- Shadow vehicles are used to warn motor vehicle traffic of the operation ahead.
Standard:
- Vehicle hazard warning signals shall not be used instead of the vehicle's high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights.
Figure 6H-17 Mobile Operations on Two-Lane Road (TA-17)
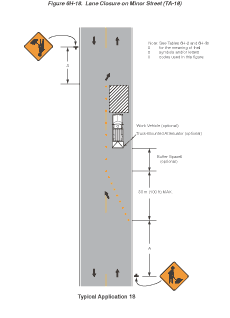
Notes for Figure 6H-18—Typical Application 18
Lane Closure on Minor Street
Standard:
- This TTC shall be used only for low-speed facilities having low traffic volumes.
Option:
- Where the work space is short, where road users can see the roadway beyond, and where volume is low, vehicular traffic may be self-regulating.
Standard:
- Where vehicular traffic cannot effectively self-regulate, one or two flaggers shall be used as illustrated in Figure 6H-10.
Option:
- Flashing warning lights and/or flags may be used to call attention to the advance warning signs.
- A truck-mounted attenuator may be used on the work vehicle and the shadow vehicle.
Figure 6H-18 Lane Closure on Minor Street (TA-18)
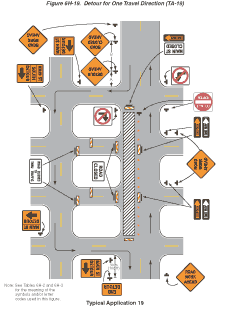
Notes for Figure 6H-19—Typical Application 19
Detour for One Travel Direction
Guidance:
- This plan should be used for streets without posted route numbers.
- On multi-lane streets, Detour signs with an Advance Turn Arrow should be used in advance of a turn.
Option:
- The STREET CLOSED legend may be used in place of ROAD CLOSED.
- Additional DO NOT ENTER signs may be used at intersections with intervening streets.
- Warning lights may be used on Type III Barricades.
- Detour signs may be located on the far side of intersections.
- A Street Name sign may be mounted with the Detour sign. The Street Name sign may be either white on green or black on orange.
Standard:
- When used, the Street Name sign shall be placed above the Detour sign.
Figure 6H-19 Detour for One Travel Direction (TA-19)
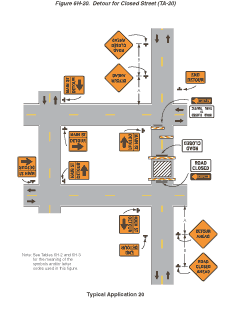
Notes for Figure 6H-20—Typical Application 20
Detour for Closed Street
Guidance:
- This plan should be used for streets without posted route numbers.
- On multi-lane streets, Detour signs with an Advance Turn Arrow should be used in advance of a turn.
Option:
- Flashing warning lights and/or flags may be used to call attention to the advance warning signs.
- Flashing warning lights may be used on Type III Barricades.
- Detour signs may be located on the far side of intersections. A Detour sign with an advance arrow may be used in advance of a turn.
- A Street Name sign may be mounted with the Detour sign. The Street Name sign may be either white on green or black on orange.
Standard:
- When used, the Street Name sign shall be placed above the Detour sign.
Support:
- See Figure 6H-9 for the information for detouring a numbered highway.
Figure 6H-20 Detour for Closed Street (TA-20)
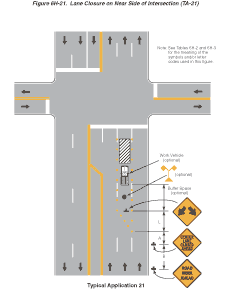
Notes for Figure 6H-21—Typical Application 21
Lane Closure on Near Side of Intersection
Standard:
- The merging taper shall direct vehicular traffic into either the right or left lane, but not both.
Guidance:
- In this typical application, a left taper should be used so that right-turn movements will not impede through motor vehicle traffic. However, the reverse should be true for left-turn movements.
- If the work space extends across a crosswalk, the crosswalk should be closed using the information and devices shown in Figure 6H-29.
Option:
- Flashing warning lights and/or flags may be used to call attention to the advance warning signs.
- A shadow vehicle with a truck-mounted attenuator may be used.
- A work vehicle with high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights may be used with the high-level warning device.
- Vehicle hazard warning signals may be used to supplement high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights.
Standard:
- Vehicle hazard warning signals shall not be used instead of the vehicle’s high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights.
Figure 6H-21 Lane Closure on Near Side of Intersection (TA-21)
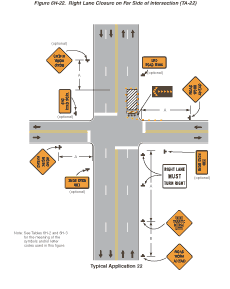
Notes for Figure 6H-22—Typical Application 22
Right Lane Closure on Far Side of Intersection
Guidance:
- If the work space extends across a crosswalk, the crosswalk should be closed using the information and devices shown in Figure 6H-29.
Option:
- The normal procedure is to close on the near side of the intersection any lane that is not carried through the intersection. However, when this results in the closure of a right lane having significant right turning movements, then the right lane may be restricted to right turns only, as shown. This procedure increases the through capacity by eliminating right turns from the open through lane.
- For intersection approaches reduced to a single lane, left-turning movements may be prohibited to maintain capacity for through vehicular traffic.
- Flashing warning lights and/or flags may be used to call attention to the advance warning signs.
- Where the turning radius is large, it may be possible to create a right-turn island using channelizing devices or pavement markings.
Figure 6H-22 Right Lane Closure on Far Side of Intersection (TA-22)
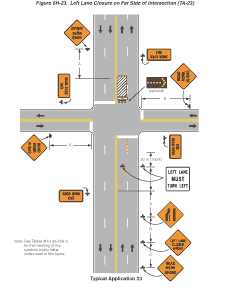
Notes for Figure 6H-23—Typical Application 23
Left Lane Closure on Far Side of Intersection
Guidance:
- If the work space extends across a crosswalk, the crosswalk should be closed using the information and devices shown in Figure 6H-29.
Option:
- Flashing warning lights and/or flags may be used to call attention to the advance warning signs.
- The normal procedure is to close on the near side of the intersection any lane that is not carried through the intersection. However, when this results in the closure of a left lane having significant left-turning movements, then the left lane may be reopened as a turn bay for left turns only, as shown.
Support:
- By first closing off the left lane and then reopening it as a turn bay, an island is created with channelizing devices that allows the LEFT LANE MUST TURN LEFT sign to be repeated on the left adjacent to the lane that it controls.
Figure 6H-23 Left Lane Closure on Far Side of Intersection (TA-23)