| FHWA Policy Memorandums |
 |
Rescinded on January 18, 2024; Superseded by the MUTCD, 11th Edition
PDF Version, 3.6MB
|
Memorandum |
| Subject: | INFORMATION AND ACTION: MUTCD – Signing for Designated Alternative Fuels Corridors |
Date: February 16, 2023 |
| From: | Mark R. Kehrli /s/ Mark R Kehrli Director, Office of Transportation Operations |
In Reply Refer To: HOTO-1 |
| To: | Federal Lands Highway Division Engineers Division Administrators |
Purpose: Through this memorandum, the Federal Highway Administration’s (FHWA) Office of Transportation Operations issues guidance regarding the signing for Alternative Fuels Corridors that have been designated by the FHWA. This action does not create a mandate for the installation of signs, but rather provides guidance on the design and appropriate use of signs for Alternative Fuels Corridors, including those funded under the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program and the Discretionary Grant Program for Charging and Fueling Infrastructure established under Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), enacted as the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA).1 Please share this information with your State transportation agencies for dissemination to their local jurisdictions. This memorandum supersedes the previous version issued December 21, 2016.2
Background: Section 1413 of the Fixing America’s Surface Transportation (FAST) Act required the U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT) to designate national plug-in electric charging, hydrogen, propane, and natural gas fueling corridors in strategic locations along major highways to improve the mobility of alternative fuel vehicles. As a follow-on to the Alternative Fuels Corridor Program established under the FAST Act, the BIL established two funding programs:
National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program. The $5 billion NEVI Formula Program will provide dedicated funding to States to strategically deploy electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure and establish an interconnected national network to facilitate data collection, access, and reliability. Initially, funding under this program is directed to designated Alternative Fuels Corridors for EVs to build out this national network, particularly along the Interstate Highway System. Funding under this program can be used for the acquisition or installation of traffic control devices located in the right-of-way to provide directional information to EV charging infrastructure acquired, installed, or operated under the NEVI Formula Program.3 Program Guidance was issued on Feb. 10, 2022.4
The FHWA also published the NEVI Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (87 FR 37262, June 22, 2022) that proposes the minimum standards and requirements regarding traffic control devices and on-premise signs for NEVI formula program and the construction of publicly accessible EV charging infrastructure under Title 23, United States Code, be set by existing applicable regulations in 23 CFR parts 655 and 750.
Discretionary Grant Program for Charging and Fueling Infrastructure. The discretionary grant program is further divided into two distinct grant programs to support EV charger deployment.
To aid in motorist recognition of such corridors, a standard identification sign and alternative fuel General Service signs have been developed that may be used along an Alternative Fuels Corridor as provided for herein.
Authority: The Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices for Streets and Highways (MUTCD) is incorporated by reference in 23 CFR part 655, Subpart F, and is the national standard for all traffic control devices installed on any street, highway, bikeway, or private road open to public travel (see definition in Section 1A.13) in accordance with 23 U.S.C. 109(d) and 402(a). As of the date of this memo, the FHWA is currently in the rulemaking process to update the MUTCD.5 The policies and procedures of FHWA to obtain basic uniformity of traffic control devices are described in 23 CFR part 655, Subpart F.6
Sign Design and Implementation: Signing for Alternative Fuels Corridors shall comply with the provisions of Part 2 of the MUTCD.7
Signs for Alternative Fuels Corridors are not required.8 Rather, States and local authorities should determine whether to use such signs on Federally-designated Alternative Fuels Corridors. This memorandum provides the sign design and other criteria for Alternative Fuels Corridor signing.9
Alternative Fuels Corridor Identification Sign
Installation of the Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign should be limited to the designated Alternative Fuels Corridor highway segment. The Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign should not be displayed along a “future,” “proposed,” or other route where alternative fueling infrastructure is incomplete, pending, or does not currently meet the established designation criteria to qualify for signing.10 Due to the limited size of these signs, the Alternative Fuels Corridor identification signs are allowed only in post-mounted roadside installations.11
The Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign assembly installation should be limited to one sign assembly at or near the beginning of the Alternative Fuels Corridor in each direction of travel. For longer corridors, additional Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign assemblies may be located beyond major intersections or major interchanges following the typical post-interchange sign sequence.12 The Alternative Fuels Corridor identification signs are not directional signs and they should not be combined with other signs, except as provided herein.
Alternative Fuels Corridor Identification Assemblies
The Alternative Fuels Corridor identification signs are used in a sign assembly with the corresponding General Service signs for the alternative fuel types designated in the corridor, except when used to mark the end of the Alternative Fuels Corridor, where the General Service signs for the alternative fuel types should not be displayed. Up to three General Service symbol signs displaying the alternative fuels available in the designated corridor may be installed below the Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign, arranged horizontally (see figure 1 of this memorandum). The size of the General Service symbol signs should not exceed 18 inches when mounted with the 24-inch Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign and 24 inches when mounted with the 36-inch Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign. When the number of eligible alternative fuels available in the corridor exceeds three, a separate plaque with the two- or three-letter designations of each of the fuels available should be used in place of the General Service symbol signs.
In accordance with the criteria established for the designation of Alternative Fuels Corridors,13 the General Service signs or plaque that may be posted in the Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign assembly are limited to the following:
Compressed Natural Gas (D9-11a, MUTCD)
Liquefied Natural Gas (D9-11d, See Attachment)
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (D9-11e, See Attachment)
Hydrogen Fuel (D9-11f, See Attachment)
Electric Vehicle Charging (D9-11b alternate design provided in MUTCD Interim Approval IA-13)
Alternative Fuels supplemental plaque with the two- or three-letter designation of each of the fuels available (D9-19aP and D9-19bP, See Attachment).
The sizes of General Service signs used elsewhere in Directional Assemblies shall comply with those provided in the MUTCD.14 General Service signs for alternative fuels may be used outside of Alternative Fuels Corridors to direct motorists to alternative fuel facilities not affiliated with a designated Alternative Fuels Corridor. The General Service symbol signs for Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), and Hydrogen fuel (HYD), shall be comprised of the fuel pump symbol of the D9-7 sign with the appropriate blue three-letter fuel abbreviation in a descending vertical alignment similar to the MUTCD Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) symbol sign (D9-11a).15
The beginning of an Alternative Fuels Corridor may be indicated with the BEGIN (M4-14) plaque with a white legend and border on a blue background mounted above the Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign in the sign assembly with the General Service signs of the fuels available in the corridor mounted below the Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign. The end of an Alternative Fuels Corridor may be indicated with an Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign with an END (M4-6) plaque with a white legend and border on a blue background mounted above it. The alternative fuels for that corridor should not be included in this sign assembly to help ensure road users do not assume there are other fuels still available, but rather understand the corridor itself has ended. The BEGIN and END plaques are not to be used to indicate where a specific fuel along the corridor begins or ends.16
Figures 3 and 4 provide examples of the use of Alternative Fuels Corridor and associated General Service sign assemblies identifying and guiding traffic to alternative fuels along a freeway alternative fuels corridor. The General Service signs for alternative fuels may also be used on any street or highway outside of an Alternative Fuels Corridor to provide directional guidance to one or more of these service facilities.
Directional Signing to Alternative Fuel Facilities—Freeways and Expressways
When the Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign is used in a designated corridor, the applicable General Service sign(s) are installed on the approach to an interchange from which the designated fuel services are available. If the services are not visible from the ramp of a single-exit interchange, the service signing are to be repeated at the intersection of the exit ramp and the crossroad.17 Where the alternative fuel facility is not located along the crossroad, additional General Service Directional Assemblies are to be installed in advance of each subsequent turn to direct road uses to the facility.18
When the distance to the next exit providing access to a particular alternative fuel is greater than a road user would likely expect, a Next Alternative Fuel sign displaying the legend, NEXT [Alternative Fuel type] XX MILES, may be used. When the distance to the next exit with EV charging service in the corridor is 50 miles or greater, the NEXT EV CHARGING XX MILES (D9-17a, See Figure 2) sign should be used.
The last availability of a particular alternative fuel type in a corridor should be indicated at the interchange on a freeway or expressway in the General Service Directional Assembly on the approach to the interchange. The LAST IN CORRIDOR (W16-19P, Attached to this memorandum) warning plaque should be included in the Directional Assembly only for the alternative fuel(s) being discontinued along the corridor.
Figures 3 and 4 provide examples of the use of Alternative Fuels Corridor and associated General Service sign assemblies identifying and directing traffic to alternative fuels along an Alternative Fuels Corridor. The General Service signs for alternative fuels may also be used on any street or highway outside of an Alternative Fuels Corridor to provide direction to one or more of these service facilities.
Directional Signing to Alternative Fuel Facilities—Conventional Roads
General Service signs may be installed in advance of facilities located directly on the designated route directing traffic into an alternative fuel facility if the on-premise business identification signs do not clearly identify the availability of the alternative fuel.
To provide positive direction to facilities not directly on the conventional road Alternative Fuels Corridor, General Service sign directional assemblies are installed at turns off the designated route to direct traffic to an alternative fuel facility along a crossroad in the vicinity of the route.19
General Considerations
Because regulatory, warning, and guide signs have a higher priority, installations of Alternative Fuels Corridor sign assemblies are to be limited to those locations where adequate spacing is available between the Alternative Fuels Corridor sign and other higher priority signs.20 Alternative Fuels Corridor signs are not to be installed in a location where they would obscure the road users’ view of other traffic control devices or distract driver’s attention from the roadway in a complex roadway environment.21
Alternative Fuels Corridor signs shall not be installed on routes other than those officially designated as Alternative Fuels Corridors, even if to provide directional information to such corridors, i.e., they shall not appear on supplemental signs or on any other information sign on or along the highway or its intersecting routes.22
If the placement of a newly installed, higher-priority traffic control device, such as a higher-priority sign, a highway traffic signal, or a temporary traffic control device, conflicts with an existing Alternative Fuels Corridor sign assembly, the Alternative Fuels Corridor sign assembly should be relocated, covered, or removed.
Conclusion: The Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign may be used by States or other highway authorities to inform motorists of an Alternative Fuels Corridor highway segment designation. Alternative Fuels Corridor identification signs are not used on corridors that have not been officially designated by the Secretary of Transportation. When used, the alternative fuels services that are part of the corridor are identified using the appropriate General Service signs, and separate General Service sign directional assemblies are used as described in this memorandum to direct road users to the facilities. As always, safety and orderly movement of traffic must be the foremost concern when installing traffic control devices and informational signs.23
Except for the statutes and regulations cited, the contents of this document do not have the force and effect of law and are not meant to bind the States or the public in any way. This document is intended only to provide information regarding existing requirements under the law or agency policies.
For more information regarding this topic, please contact Mr. Martin Calawa, Office of Transportation Operations, at Martin.Calawa@dot.gov.
Attachments cc:
Associate Administrators Chief Counsel
Chief Financial Officer
Chief Technical Services Officer Directors of Field Services

D18-1 Alternative Fuels Corridor Long Description
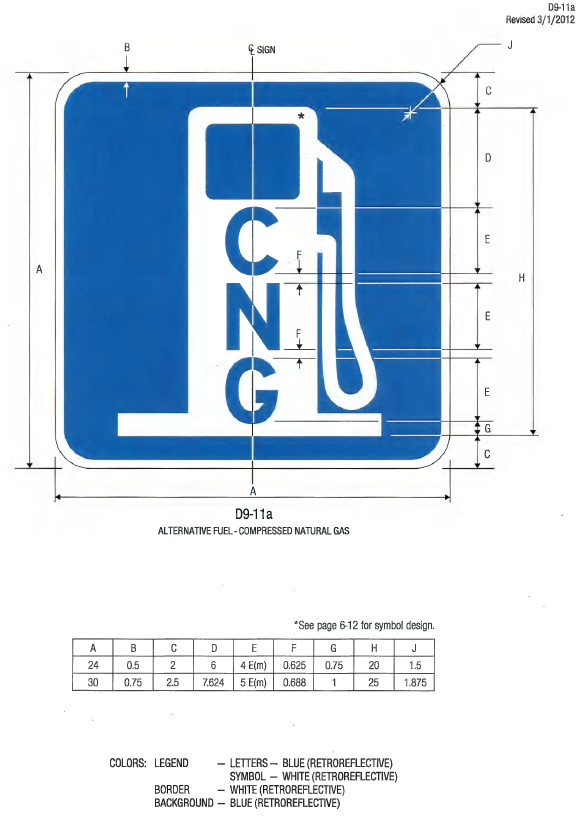
D9-11a Alternative Fuel - Compressed Natural Gas Long Description
D9-11b (Alternate) Electric Vehicle Charging (Alternate Symbol) Long Description
D9-11d Alternative Fuel - Liquefied Natural Gas Long Description
D9-11e Alternative Fuel - Liquefied Petroleum Gas Long Description
D9-11f Alternative Fuel - Hydrogen Long Description
D9-11GP Alternative 4-Fuels (Plaque) Long Description
D9-11HP Alternative 5-Fuels (Plaque) Long Description
W26-1 Last in Corridor (Plaque) Long Description
1 Pub. L. 117-58 (Nov. 15, 2021)
2 “Information and Action: MUTCD – Signing for Designated Alternative Fuels Corridors.” FHWA (Dec. 21, 2016).
3 Paragraph (2) under the Highway Infrastructure Program heading in title VIII of division J of BIL, Pub. L. 117-58 (Nov. 15, 2021). NOTE: While directional signs and sign assemblies to alternative fuel services are eligible for funding under NEVI, the Alternative Fuels Corridor identification sign and assemblies are not.
4 https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/environment/alternative_fuel_corridors/nominations/90d_nevi_formula_program_guidance.pdf.
5 Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices for Streets and Highways (MUTCD), 2009 Edition with Revisions 1, 2, and 3 (July 2022), rulemaking currently underway see: https://www.reginfo.gov/public/do/eAgendaViewRule?pubId=202204&RIN=2125-AF85.
6 MUTCD Intro. ¶ 02 at I-1
7 MUTCD Intro. ¶¶ 01-03 at I-1; § 2
8 NEVI Program Guidance containing information on funding for signing leading to NEVI funded facilities can be found here: https://www.fhwa.dot.gov/environment/alternative_fuel_corridors/nominations/90d_nevi_formula_program_guidance.pdf.
9 Id.
10 The FHWA’s Office of Planning, Environment, and Realty has established the qualifying criteria and designations. See 81 FR 47850 (July 22, 2016).
11 MUTCD § 2A.11, Table 2E-2
12 MUTCD § 2E.38, 2009 Ed.
13 23 U.S.C. 151; Pub. L. 114-94 (Dec. 4, 2015).
14 MUTCD § 2I.02, ¶ 02-03, Fig. 2I-1 at 300-301
15 MUTCD Intro. ¶¶ 01-03 at I-1
16 MUTCD § 2D.22, ¶ 02 and § 2D.23, ¶ 02
17 MUTCD § 2I.03, ¶ 02
18 MUTCD § 2I.03, ¶ 02
19 MUTCD § 2I.03, ¶ 02
20 MUTCD § 2H.08, ¶ 03
21 MUTCD § 2A.16, ¶ 03
22 Id.
23 MUTCD Intro. ¶¶ 01-03 at I-1; § 1A
|
United States Department of Transportation - Federal Highway Administration |
||