Chapter 3C. Object Markers
Section 3C.01 Object Marker Design and Placement Height
Support:
Object markers are used to mark obstructions within or adjacent
to the roadway.
Standard:
When used, object markers (see Figure 3C-1) shall consist of an
arrangement of one or more of the following types:
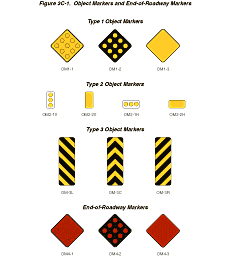
Type 1—either a marker consisting of nine yellow retroreflectors, each with a minimum diameter of 75 mm (3 in), mounted symmetrically on a yellow (OM1-1) or black (OM1-2) diamond panel 450 mm (18 in) or more on a side; or on an all-yellow retroreflective diamond panel (OM1-3) of the same size.
Type 2—either a marker (OM2-1V or OM2-1H) consisting of three yellow retroreflectors, each with a minimum diameter of 75 mm (3 in), arranged either horizontally or vertically on a white panel measuring at least 150 x 300 mm (6 x 12 in), or on an all-yellow horizontal or vertical retroreflective panel (OM2-2V or OM2-2H), measuring at least 150 x 300 mm (6 x 12 in).
Type 3—a striped marker, 300 x 900 mm (12 x 36 in), consisting of a vertical rectangle with alternating black and retroreflective yellow stripes sloping downward at an angle of 45 degrees toward the side of the obstruction on which traffic is to pass. The minimum width of the yellow and black stripes shall be 75 mm (3 in).
Figure 3C-1 Object Markers and End-of-Roadway Markers
Support:
A better appearance can be achieved if the black stripes are wider
than the yellow stripes.
Type 3 object markers with stripes that begin at the upper right side and slope downward to the lower left side are designated as right object markers (OM-3R). Object markers with stripes that begin at the upper left side and slope downward to the lower right side are designated as left object markers (OM-3L).
Guidance:
When used for marking objects in the roadway or objects that are
2.4 m (8 ft) or less from the shoulder or curb, the mounting height
to the bottom of the object marker should be at least 1.2 m (4 ft)
above the surface of the nearest traffic lane.
When used to mark objects more than 2.4 m (8 ft) from the shoulder or curb, the mounting height to the bottom of the object marker should be at least 1.2 m (4 ft) above the ground.
Option:
When object markers or markings are applied to an object that by
its nature requires a lower or higher mounting, the vertical mounting
height may vary according to need.
Section 3C.02 Markings for Objects in the Roadway
Standard:
Obstructions within the roadway shall be marked with a Type 1 or
Type 3 object marker. In addition to markers on the face of the
obstruction, warning of approach to the obstruction shall be given
by appropriate pavement markings (see Section
3B.10).
Option:
To provide additional emphasis, large surfaces such as bridge piers
may be painted with diagonal stripes, 300 mm (12 in) or greater
in width, similar in design to the Type 3 object marker.
Standard:
The alternating black and retroreflective yellow stripes (OM-3L,
OM-3R) shall be sloped down at an angle of 45 degrees toward the
side on which traffic is to pass the obstruction. If traffic can
pass to either side of the obstruction, the alternating black and
retroreflective yellow stripes (OM-3C) shall form chevrons that
point upwards.
Option:
Appropriate signs (see Sections 2B.33
and 2C.20)
directing traffic to one or both sides of the obstruction may be
used instead of the object marker.
Section 3C.03 Markings for Objects Adjacent to the Roadway
Support:
Objects not actually in the roadway are sometimes so close to the
edge of the road that they need a marker. These include underpass
piers, bridge abutments, handrails, and culvert headwalls. In other
cases there might not be a physical object involved, but other roadside
conditions exist, such as narrow shoulders, drop-offs, gores, small
islands, and abrupt changes in the roadway alignment, that might
make it undesirable for a road user to leave the roadway, and therefore
would create a need for a marker.
Option:
Type 2 or Type 3 object markers may be used at locations such as
those described in the preceding Support paragraph.
Standard:
If used, the inside edge of the marker shall be in line with
the inner edge of the obstruction.
Guidance:
Standard warning signs (see Chapter 2C) should also be used where
applicable.
Section 3C.04 End-of-Roadway Markers
Support:
The end-of-roadway marker is used to warn and alert road users of
the end of a roadway in other than construction or maintenance areas.
Standard:
The end-of-roadway marker (see Figure 3C-1) shall be one of the
following: a marker consisting of nine red retroreflectors, each
with a minimum diameter of 75 mm (3 in), mounted symmetrically on
a red (OM4-1) or black (OM4-2) diamond panel 450 mm (18 in) or more
on a side; or a retroreflective red diamond panel (OM4-3) 450 mm
(18 in) or more on a side.
Option:
The end-of-roadway marker may be used in instances where there are
no alternate vehicular paths.
Where conditions warrant, more than one marker, or a larger marker with or without a Type III barricade (see Section 3F.01), may be used at the end of the roadway.
Standard:
The minimum mounting height to the bottom of an end-of-roadway marker
shall be 1.2 m (4 ft) above the edge of the pavement.
Guidance:
Appropriate advance warning signs (see Chapter
2C) should be used.
