Chapter 3D. Delineators
Section 3D.01 Delineators
Support:
Delineators are particularly beneficial at locations where the alignment
might be confusing or unexpected, such as at lane reduction transitions
and curves. Delineators are effective guidance devices at night
and during adverse weather. An important advantage of delineators
in certain locations is that they remain visible when the roadway
is wet or snow covered.
Delineators are considered guidance devices rather than warning devices.
Option:
Delineators may be used on long continuous sections of highway
or through short stretches where there are changes in horizontal
alignment.
Section 3D.02 Delineator Design
Standard:
Delineators shall be retroreflective devices mounted above the roadway
surface and along the side of the roadway in a series to indicate
the alignment of the roadway. Delineators shall consist of retroreflector
units that are capable of clearly retroreflecting light under normal
atmospheric conditions from a distance of 300 m (1,000 ft) when
illuminated by the high beams of standard automobile lights.
Retroreflective elements for delineators shall have a minimum dimension of 75 mm (3 in).
Option:
Elongated retroreflective units of appropriate size may be used
in place of two retroreflectors mounted as a unit.
Section 3D.03 Delineator Application
Standard:
The color of delineators shall conform to the color of edge lines
stipulated in Section 3B.06.
Single delineators shall be provided on the right side of freeways and expressways and on at least one side of interchange ramps, except in the following cases:
- On tangent sections of freeways and expressways when all
of the following conditions are met:
- Raised pavement markers are used continuously on lane lines throughout all curves and on all tangents to supplement pavement markings.
- Where whole routes or substantial portions of routes have large sections of tangent alignment.
- Roadside delineators are used to lead into all curves.
- On sections of roadways where continuous lighting is in operation between interchanges.
Option:
Delineators may be provided on other classes of roads. Single delineators
may be provided on the left side of roadways.
Guidance:
Single delineators should be provided on the outside of curves on
interchange ramps.
Where median crossovers are provided for official or emergency use on divided highways and where these crossovers are to be marked, a double yellow delineator should be placed on the left side of the through roadway on the far side of the crossover for each roadway.
Double or vertically elongated delineators should be installed at 30 m (100 ft) intervals along acceleration and deceleration lanes.
Option:
Red delineators may be used on the reverse side of any delineator
where it would be viewed by a road user traveling in the wrong direction
on that particular ramp or roadway.
Delineators of the appropriate color may be used to indicate a lane reduction transition where either an outside or inside lane merges into an adjacent lane.
Guidance:
For lane reduction transitions, the delineators should be used adjacent
to the lane or lanes reduced for the full length of the transition
and should be so placed and spaced to show the reduction (see Figure
3B-12).
Support:
Delineators are not necessary for traffic moving in the direction
of a wider pavement or on the side of the roadway where the alignment
is not affected by the lane reduction transition.
Guidance:
On a highway with continuous delineation on either or both sides,
delineators should be carried through transitions.
Option:
On a highway with continuous delineation on either or both sides,
the spacing between a series of delineators may be closer.
Standard:
When used on a truck escape ramp, delineators shall be red.
Guidance:
Red delineators should be placed on both sides of truck escape ramps.
The delineators should be spaced at 15 m (50 ft) intervals for a
distance sufficient to identify the ramp entrance. Delineator spacing
beyond the ramp entrance should be adequate for guidance according
to the length and design of the escape ramp.
Section 3D.04 Delineator Placement and Spacing
Guidance:
Delineators should be mounted on suitable supports so that the top
of the highest retroreflector is 1.2 m (4 ft) above the near roadway
edge. They should be placed 0.6 to 2.4 m (2 to 8 ft) outside the
outer edge of the shoulder, or if appropriate, in line with the
roadside barrier that is 2.4 m (8 ft) or less outside the outer
edge of the shoulder.
Delineators should be placed at a constant distance from the edge of the roadway, except that where an obstruction intrudes into the space between the pavement edge and the extension of the line of the delineators, the delineators should be transitioned to be in line with or inside the innermost edge of the obstruction. If the obstruction is a guardrail, the delineators should be transitioned to be either just behind, directly above (in line with), or on the innermost edge of the guardrail.
Delineators should be spaced 60 to 160 m (200 to 530 ft) apart on mainline tangent sections. Delineators should be spaced 30 m (100 ft) apart on ramp tangent sections.
Support:
Examples of delineator installations are shown in Figure 3D-1.
Figure 3D-1 Examples of Delineator Placement
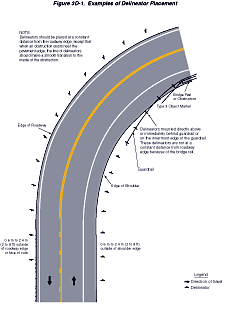
Option:
When uniform spacing is interrupted by such features as driveways
and intersections, delineators which would ordinarily be located
within the features may be relocated in either direction for a distance
not exceeding one quarter of the uniform spacing. Delineators still
falling within such features may be eliminated.
Delineators may be transitioned in advance of a lane transition or obstruction as a guide for oncoming traffic.
Guidance:
The spacing of delineators should be adjusted on approaches to and
throughout horizontal curves so that several delineators are always
simultaneously visible to the road user. The approximate spacing
shown in Table 3D-1 should be used.
Spacing for specific radii may be interpolated from table. The minimum spacing should be 6.1m (20 ft). The spacing on curves should not exceed 90 m (300 ft). In advance of or beyond a curve, and proceeding away from the end of the curve, the spacing of the first delineator is 2S, the second 3S, and the third 6S but not to exceed 90 m (300 ft). S refers to the delineator spacing for specific radii computed from the formula
