Chapter 2A. General
Section 2A.01 Function and Purpose of Signs
Support:
This Manual contains Standards, Guidance, and Options for the signing
within the right-of-way of all types of highways open to public
travel. The functions of signs are to provide regulations, warnings,
and guidance information for road users. Both words and symbols
are used to convey the messages. Signs are not typically used to
confirm rules of the road.
Detailed sign requirements are located in the following
Chapters of Part 2:
Chapter 2B—Regulatory Signs
Chapter 2C—Warning Signs
Chapter 2D—Guide Signs (Conventional
Roads)
Chapter 2E—Guide Signs (Freeways
and Expressways)
Chapter 2F—Specific Service (Logo)
Signs
Chapter 2G—Tourist-Oriented Direction
Signs
Chapter 2H—Recreational and Cultural
Interest Area Signs
Chapter 2I—Emergency Management Signs
Standard:
Because the requirements and standards for signs depend on the particular
type of highway upon which they are to be used, the following definitions
shall apply:
- Freeway—a divided highway with full control of access;
- Expressway—a divided highway with partial control of access;
- Conventional Road—a street or highway other than a low-volume road (as defined in Section 5A.01), a freeway, or an expressway; and
- Special Purpose Road—a low-volume, low-speed road that serves recreational areas or resource development activities, or that provides local access.
Section 2A.02 Definitions
Support:
Definitions that are applicable to signs are given in Sections 1A.13
and 2A.01.
Section 2A.03 Standardization of Application
Support:
It is recognized that urban traffic conditions differ from those
in rural environments, and in many instances signs are applied and
located differently. Where pertinent and practical, this Manual
sets forth separate recommendations for urban and rural conditions.
Guidance:
Signs should be used only where justified by engineering judgment
or studies, as noted in Section
1A.09.
Results from traffic engineering studies of physical and traffic factors should indicate the locations where signs are deemed necessary or desirable.
Roadway geometric design and sign application should be coordinated so that signing can be effectively placed to give the road user any necessary regulatory, warning, guidance, and other information.
Standard:
Each standard sign shall be displayed only for the specific purpose
as prescribed in this Manual. Determination of the particular signs
to be applied to a specific condition shall be made in accordance
with the criteria set forth in Part 2. Before any new highway, detour,
or temporary route is opened to traffic, all necessary signs shall
be in place. Signs required by road conditions or restrictions shall
be removed when those conditions cease to exist or the restrictions
are withdrawn.
Section 2A.04 Excessive Use of Signs
Guidance:
Regulatory and warning signs should be used conservatively because
these signs, if used to excess, tend to lose their effectiveness.
If used, route signs and directional signs should be used frequently
because they promote reasonably safe and efficient operations by
keeping road users informed of their location.
Section 2A.05 Classification of Signs
Standard:
Signs shall be defined by their function as follows:
- Regulatory signs give notice of traffic laws or regulations.
- Warning signs give notice of a situation that might not be readily apparent.
- Guide signs show route designations, destinations, directions, distances, services, points of interest, and other geographical, recreational, or cultural information.
Section 2A.06 Design of Signs
Support:
This Manual shows many typical standard signs approved for use on
streets, highways, bikeways, and pedestrian crossings.
In the specifications for individual signs, the general appearance of the legend, color, and size are shown in the accompanying tables and illustrations, and are not always detailed in the text.
Detailed drawings of standard signs and alphabets are shown in the "Standard Highway Signs" book. Section 1A.11 contains information regarding how to obtain this publication.
The basic requirements of a highway sign are that it be legible to those for whom it is intended and that it be understandable in time to permit a proper response. Desirable attributes include:
- High visibility by day and night; and
- High legibility (adequately sized letters or symbols, and a short legend for quick comprehension by a road user approaching a sign).
Standardized colors and shapes are specified so that the several classes of traffic signs can be promptly recognized. Simplicity and uniformity in design, position, and application are important.
Standard:
The term legend shall include all word messages and symbol designs
that are intended to convey specific meanings.
Uniformity in design shall include shape, color, dimensions, legends, borders, and illumination or retroreflectivity.
Where a standard word message is applicable, the wording shall be as herein provided. Standardization of these designs does not preclude further improvement by minor changes in the proportion or orientation of symbols, width of borders, or layout of word messages, but all shapes and colors shall be as indicated.
In situations where word messages are required other than those herein provided, the signs shall be of the same shape and color as standard signs of the same functional type.
Except as stated in the Option below, Internet addresses shall not be shown on any sign, supplemental plaque, sign panel (including logo panels on specific service signs), or changeable message sign.
Guidance:
Unless otherwise stated in this Manual for a specific sign, and
except as stated in the Option below, phone numbers of more than
four characters should not be shown on any sign, supplemental plaque,
sign panel (including logo panels on specific service signs), or
changeable message sign.
Option:
Internet addresses or phone numbers with more than four characters
may be shown on signs, supplemental plaques, sign panels, and changeable
message signs that are intended for viewing only by pedestrians,
bicyclists, occupants of parked vehicles, or drivers of vehicles
on low-speed roadways where engineering judgment indicates that
drivers can reasonably safely stop out of the traffic flow to read
the message.
State and local highway agencies may develop special word message signs in situations where roadway conditions make it necessary to provide road users with additional regulatory, warning, or guidance information.
Section 2A.07 Changeable Message Signs
Standard:
To the extent practical, changeable message signs, which are traffic
control devices designed to display variable messages, shall conform
to the principles established in this Manual, and with the design
and applications prescribed in Sections 2E.21,
6F.02,
and 6F.55.
Guidance:
Except for safety or transportation-related messages, changeable
message signs should not be used to display information other than
regulatory, warning, and guidance information related to traffic
control.
Support:
Changeable message signs, with more sophisticated technologies,
are gaining widespread use to inform road users of variable situations,
particularly along congested traffic corridors. Highway and transportation
organizations are encouraged to develop and experiment (see Section
1A.10) with changeable message signs and to carefully evaluate
such installations so that experience is gained toward adoption
of future standards.
Information regarding the design and application of portable changeable message signs in temporary traffic control zones is contained in Section 6F.55. Section 1A.14 contains information regarding the use of abbreviations on traffic control devices, including changeable message signs.
Option:
Changeable message signs (including portable changeable message
signs) that display a regulatory or warning message may use a black
background with a white, yellow, orange, red, or fluorescent yellow-green
legend as appropriate, except where specifically restricted in this
Manual for a particular sign.
Changeable message signs, both permanent and portable, may be used by State and local highway agencies to display safety or transportation-related messages. State and local highway agencies may develop and establish a policy regarding the display of safety and transportation-related messages on permanent and changeable message signs that specifies the allowable messages and applications, consistent with the provisions of this Manual.
Support:
Examples of safety messages include SEAT BELTS BUCKLED? and DON'T
DRINK AND DRIVE. Examples of transportation-related messages include
STADIUM EVENT SUNDAY, EXPECT DELAYS NOON TO 4 PM and OZONE ALERT
CODE RED—USE TRANSIT.
Guidance:
When a changeable message sign is used to display a safety or transportation-related
message, the requirements of Section 6F.55 should be followed. The
message should be simple, brief, legible, and clear. A changeable
message sign should not be used to display a safety or transportation-related
message if doing so would adversely affect the respect for the sign.
"CONGESTION AHEAD" or other overly simplistic or vague messages
should not be displayed alone. These messages should be supplemented
with a message on the location or distance to the congestion or
incident, how much delay is expected, alternative route, or other
similar messages.
Standard: When a changeable message sign is used to display a safety or transportation related message, the display format shall not be of a type that could be considered similar to advertising displays. The display format shall not include animation, rapid flashing, or other dynamic elements that are characteristic of sports scoreboards or advertising displays.
Section 2A.08 Retroreflectivity and Illumination
Support:
There are many materials currently available for retroreflection
and various methods currently available for the illumination of
signs. New materials and methods continue to emerge. New materials
and methods can be used as long as the signs meet the standard requirements
for color, both by day and by night.
Standard:
Regulatory, warning, and guide signs shall be retroreflective or
illuminated to show the same shape and similar color by both day
and night, unless specifically stated otherwise in the text discussion
in this Manual of a particular sign or group of signs.
The requirements for sign illumination shall not be considered to be satisfied by street or highway lighting.
Guidance:
All overhead sign installations should be illuminated unless an
engineering study shows that retroreflection will perform effectively
without illumination.
Option:
Sign elements may be illuminated by the means shown in Table 2A-1.
Retroreflection of sign elements may be accomplished by the means
shown in Table 2A-2.
Light Emitting Diode (LED) units may be used individually within the face of a sign and in the border of a sign, except for Changeable Message Signs, to improve the conspicuity, increase the legibility of sign legends and borders, or provide a changeable message. Individual LED pixels may be used in the border of a sign.
Standard:
If used, the LEDs shall be the same color as the sign legend, border,
or background. If flashed, all LED units shall flash simultaneously
at a rate of more than 50 and less than 60 times per minute. The
uniformity of the sign design shall be maintained without any decrease
in visibility, legibility, or driver comprehension during either
daytime or nighttime conditions.
A module of multiple LED units used as a closely-spaced, single light source shall only be used within the sign face for legends or symbols.
Support:
Information regarding the use of retroreflective material on the
sign support is contained in Section 2A.21.
Section 2A.09 Maintaining Minimum Retroreflectivity
Support:
Retroreflectivity is one of several factors associated with maintaining
nighttime sign visibility (see Section 2A.22).
Standard:
Public agencies or officials having jurisdiction shall use an assessment or management method
that is designed to maintain sign retroreflectivity at or above the minimum levels in Table 2A-3.
| Sign Color | Sheeting Type (ASTM D4956-04) | Additional Criteria | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beaded Sheeting | Prismatic Sheeting | ||||
| I | II | III | III, IV, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X | ||
| White on Green | W*; G ≥ 7 | W*; G ≥ 15 | W*; G ≥ 25 | W ≥ 250; G ≥ 25 | Overhead |
| W*; G ≥ 7 | W ≥ 120; G ≥ 15 | Ground-mounted | |||
| Black on Yellow or Black on Orange |
Y*; O* | Y ≥ 50; O ≥ 50 | 2 | ||
| Y*; O* | Y ≥ 75; O ≥ 75 | 3 | |||
| White on Red | W ≥ 35; R ≥ 7 | 4 | |||
| Black on White | W ≥ 50 | — | |||
Notes: |
|||||
| Bold Symbol Signs | |||||
|
|
|
|||
| Fine Symbol Signs – Symbol signs not listed as Bold Symbol Signs. | |||||
| Special Cases | |||||
|
|||||
Support:
Compliance with the above Standard is achieved by having a method in place and using the method
to maintain the minimum levels established in Table 2A-3. Provided that an assessment or
management method is being used, an agency or official having jurisdiction would be in compliance
with the above Standard even if there are some individual signs that do not meet the minimum
retroreflectivity levels at a particular point in time.
Guidance: Except for those signs specifically identified in the Option in this Section, one or more of the following assessment or management methods should be used to maintain sign retroreflectivity:
- Visual Nighttime Inspection – The retroreflectivity of an existing sign is assessed by a trained sign inspector conducting a visual inspection from a moving vehicle during nighttime conditions. Signs that are visually identified by the inspector to have retroreflectivity below the minimum levels should be replaced.
- Measured Sign Retroreflectivity – Sign retroreflectivity is measured using a retroreflectometer. Signs with retroreflectivity below the minimum levels should be replaced.
- Expected Sign Life – When signs are installed, the installation date is labeled or recorded so that the age of a sign is known. The age of the sign is compared to the expected sign life. The expected sign life is based on the experience of sign retroreflectivity degradation in a geographic area compared to the minimum levels. Signs older than the expected life should be replaced.
- Blanket Replacement – All signs in an area/corridor, or of a given type, should be replaced at specified intervals. This eliminates the need to assess retroreflectivity or track the life of individual signs. The replacement interval is based on the expected sign life, compared to the minimum levels, for the shortest life material used on the affected signs.
- Control Signs – Replacement of signs in the field is based on the performance of a sample of control signs. The control signs might be a small sample located in a maintenance yard or a sample of signs in the field. The control signs are monitored to determine the end of retroreflective life for the associated signs. All field signs represented by the control sample should be replaced before the retroreflectivity levels of the control sample reach the minimum levels.
- Other Methods – Other methods developed based on engineering studies can be used.
Support:
Additional information about these methods is contained in the 2007 Edition of FHWA's "Maintaining Traffic Sign Retroreflectivity" (see Section 1A.11).
Option: Highway agencies may exclude the following signs from the retroreflectivity maintenance guidelines described in this Section:
- Parking, Standing, and Stopping signs (R7 and R8 series)
- Walking/Hitchhiking/Crossing signs (R9 series, R10-1 through R10-4b)
- Adopt-A-Highway signs
- All signs with blue or brown backgrounds
- Bikeway signs that are intended for exclusive use by bicyclists or pedestrians
Section 2A.10 Shapes
Standard:
Particular shapes, as shown in Table 2A-4, shall be used exclusively
for specific signs or series of signs, unless specifically stated otherwise
in the text discussion in this Manual for a particular sign or class
of signs.
| Shape |
Signs |
|---|---|
| Octagon |
* Stop |
| Equilateral
Triangle (1 point down) |
* Yield |
| Circle |
* Highway-Rail Grade Crossing (Advance Warning) |
| Pennant
Shape/ Isosceles Triangle (longer axis horizontal) |
* No Passing |
| Pentagon (pointed up) | * School Advance
Warning Sign * County Route Sign |
| Crossbuck (two rectangles in an "X" configuration) |
* Highway-Rail Grade Crossing |
| Diamond | Warning Series |
| Rectangle (including square) | Regulatory Series ** Guide Series Warning Series |
| Trapezoid | Recreational
and Cultural Interest Area Series National Forest Route Sign |
** Guide series includes general service, specific service, recreation, and emergency management signs
Section 2A.11 Sign Colors
Standard:
The colors to be used on standard signs and their specific use on
these signs shall be as indicated in the applicable Sections of
this Manual. The color coordinates and values shall be as described
in 23 CFR, Part 655, Subpart F, Appendix.
Support:
As a quick reference, common uses of sign colors are shown in Table
2A-5. Color schemes on specific signs are shown in the illustrations
located in each appropriate Section.
Whenever white is specified herein as a color, it is understood to include silver-colored retroreflective coatings or elements that reflect white light.
The colors coral, purple, and light blue are being reserved for uses that will be determined in the future by the Federal Highway Administration.
Information regarding color coding of destinations on guide signs is contained in Section 2D.03.
Section 2A.12 Dimensions
Support:
Sign sizes for use on the different classes of highways are shown
in Sections 2B.03,
2C.04,
2D.04,
5A.03,
6F.02,
7B.01,
8B.02,
and 9B.02
and in the "Standard Highway Signs" book.
The "Standard Highway Signs" book (see Section 1A.11) prescribes design details for up to five different sizes depending on the type of traffic facility, including bikeways. Smaller sizes are designed to be used on bikeways and some other off-road applications. Larger sizes are designed for use on freeways and expressways, and can also be used to enhance road user safety and convenience on other facilities, especially on multi-lane divided highways and on undivided highways having five or more lanes of traffic and/or high speeds. The intermediate sizes are designed to be used on other highway types.
Standard:
The sign dimensions prescribed in this Manual and in the "Standard
Highway Signs" book shall be used unless engineering judgment
determines that other sizes are appropriate. Where engineering judgment
determines that sizes smaller than the prescribed dimensions are
appropriate for use, the sign dimensions shall not be less than
the minimum dimensions specified in this Manual. Where engineering
judgment determines that sizes larger than the prescribed dimensions
are appropriate for use, standard shapes and colors shall be used
and standard proportions shall be retained as much as practical.
Guidance:
Increases above the prescribed sizes should be used where greater
legibility or emphasis is needed. Wherever practical, the overall
sign dimensions should be increased in 150 mm (6 in) increments.
Section 2A.13 Symbols
Support:
Sometimes a change from word messages to symbols requires significant
time for public education and transition. Therefore, this Manual
includes the practice of using educational plaques to accompany
some new symbol signs.
Standard:
Symbol designs shall in all cases be unmistakably similar to those
shown in this Manual and in the "Standard Highway Signs"
book (see Section 1A.11). New symbol designs shall be adopted by
the Federal Highway Administration based on research evaluations
to determine road user comprehension, sign conspicuity, and sign
legibility.
Guidance:
New warning or regulatory symbol signs not readily recognizable
by the public should be accompanied by an educational plaque.
Option:
State and/or local highway agencies may conduct research studies
to determine road user comprehension, sign conspicuity, and sign
legibility.
Educational plaques may be left in place as long as they are in serviceable condition.
Although most standard symbols are oriented facing left, mirror images of these symbols may be used where the reverse orientation might better convey to road users a direction of movement.
Section 2A.14 Word Messages
Standard:
Except as noted in Section 2A.06, all
word messages shall use standard wording and letters as shown in
this Manual and in the "Standard Highway Signs" book (see
Section 1A.11).
Guidance:
Word messages should be as brief as possible and the lettering should
be large enough to provide the necessary legibility distance. A
minimum specific ratio, such as 25 mm (1 in) of letter height per
12 m (40 ft) of legibility distance, should be used.
Support:
Some research indicates that a ratio of 25 mm (1 in) of letter height
per 10 m (33 ft) of legibility distance could be beneficial.
Guidance:
Abbreviations (see Section
1A.14) should be kept to a minimum, and should include only
those that are commonly recognized and understood, such as AVE (for
Avenue), BLVD (for Boulevard), N (for North), or JCT (for Junction).
Standard:
All sign lettering shall be in capital letters as provided in the
"Standard Highway Signs" book, except as indicated in
the Option below.
Option:
Word messages on street name signs and destinations on guide signs
may be composed of a combination of lower-case letters with initial
upper-case letters.
Section 2A.15 Sign Borders
Standard:
Unless specifically stated otherwise, each sign illustrated herein
shall have a border of the same color as the legend, at or just
inside the edge.
The corners of all sign borders shall be rounded, except for STOP signs.
Guidance:
A dark border on a light background should be set in from the edge,
while a light border on a dark background should extend to the edge
of the panel. A border for 750 mm (30 in) signs with a light background
should be from 13 to 19 mm (0.5 to 0.75 in) in width, 13 mm (0.5
in) from the edge. For similar signs with a light border, a width
of 25 mm (1 in) should be used. For other sizes, the border width
should be of similar proportions, but should not exceed the stroke-width
of the major lettering of the sign. On signs exceeding 1800 x 3000
mm (72 x 120 in) in size, the border should be 50 mm (2 in) wide,
or on larger signs, 75 mm (3 in) wide. Except for STOP signs and
as otherwise provided in Section 2E.15, the corners of the sign
should be rounded to fit the border.
Section 2A.16 Standardization of Location
Support:
Standardization of position cannot always be attained in practice.
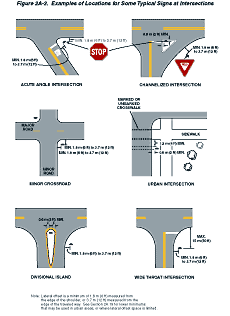
Examples of heights and lateral locations of signs for typical installations
are illustrated in Figure 2A-1, and examples of locations for some
typical signs at intersections are illustrated in Figure 2A-2.
Figure 2A-1 Examples of Heights and Lateral Locations of Signs for Typical Installations
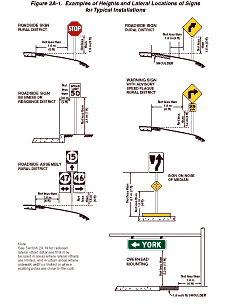
Figure 2A-2 Examples of Locations for Some Typical Signs at Intersections
Standard:
Signs requiring different decisions by the road user shall be spaced
sufficiently far apart for the required decisions to be made reasonably
safely. One of the factors considered when determining the appropriate
spacing shall be the posted or 85th-percentile speed.
Guidance:
Signs should be located on the right side of the roadway where they
are easily recognized and understood by road users. Signs in other
locations should be considered only as supplementary to signs in
the normal locations, except as otherwise indicated.
Signs should be individually installed on separate posts or mountings except where:
- One sign supplements another, or
- Route or directional signs are grouped to clarify information to motorists, or
- Regulatory signs that do not conflict with each other are grouped, such as turn prohibition signs posted with one-way signs, street name signs posted with a stop or yield sign, or a parking regulation sign posted with a speed limit sign.
Signs should be located so that they:
- Are outside the clear zone unless placed on a breakaway or yielding support (see Section 2A.19);
- Optimize nighttime visibility;
- Minimize the effects of mud splatter and debris;
- Do not obscure each other; and
- Are not hidden from view.
Support:
The clear zone is the total roadside border area, starting at the
edge of the traveled way, available for use by errant vehicles.
The width of the clear zone is dependent upon traffic volumes, speeds,
and roadside geometry. Additional information can be found in the
"AASHTO Roadside Design Guide" (see Addresses
for AASHTO's address).
Guidance:
With the increase in traffic volumes and the desire to provide road
users regulatory, warning, and guidance information, an order of
priority for sign installation should be established.
Support:
An order of priority is especially critical where space is limited
for sign installation and there is a demand for several different
types of signs. Overloading road users with too much information
is not desirable.
Guidance:
Because regulatory and warning information is more critical to the
road user than guidance information, regulatory and warning signing
whose location is critical should be displayed rather than guide
signing in cases where conflicts occur. Information of a less critical
nature should be moved to less critical locations or omitted.
Option:
Under some circumstances, such as on curves to the right, signs
may be placed on median islands or on the left side of the road.
A supplementary sign located on the left of the roadway may be used
on a multi-lane road where traffic in the right lane might obstruct
the view to the right.
Guidance:
In urban areas where crosswalks exist, signs should not be placed
within 1.2 m (4 ft) in advance of the crosswalk.
Section 2A.17 Overhead Sign Installations
Guidance:
Overhead signs should be used on freeways and expressways, at locations
where some degree of lane-use control is desirable, and at locations
where space is not available at the roadside.
Support:
The operational requirements of the present highway system are such
that overhead signs have value at many locations. The factors to
be considered for the installation of overhead sign displays are
not definable in specific numerical terms.
Option:
The following conditions (not in priority order) may be considered
in an engineering study to determine if overhead signs would be
beneficial:
- Traffic volume at or near capacity;
- Complex interchange design;
- Three or more lanes in each direction;
- Restricted sight distance;
- Closely spaced interchanges;
- Multi-lane exits;
- Large percentage of trucks;
- Street lighting background;
- High-speed traffic;
- Consistency of sign message location through a series of interchanges;
- Insufficient space for ground-mounted signs;
- Junction of two freeways; and
- Left exit ramps.
Over-crossing structures may serve for the support of overhead signs, and under some circumstances, may be the only practical solution that will provide adequate viewing distance. Use of such structures as sign supports may eliminate the need for the foundations and sign supports along the roadside.
Section 2A.18 Mounting Height
Support:
The provisions of this Section apply unless specifically stated
otherwise for a particular sign elsewhere in this Manual.
Standard:
Signs installed at the side of the road in rural districts shall
be at least 1.5 m (5 ft), measured from the bottom of the sign to
the near edge of the pavement.
Where parking or pedestrian movements occur, the clearance to the bottom of the sign shall be at least 2.1 m (7 ft).
Directional signs on freeways and expressways shall be installed with a minimum height of 2.1 m (7 ft). If a secondary sign is mounted below another sign, the major sign shall be installed at least 2.4 m (8 ft) and the secondary sign at least 1.5 m (5 ft) above the level of the pavement edge. All route signs, warning signs, and regulatory signs on freeways and expressways shall be at least 2.1 m (7 ft) above the level of the pavement edge.
Option:
The height to the bottom of a secondary sign mounted below another
sign may be 0.3 m (1 ft) less than the height specified above.
Where signs are placed 9 m (30 ft) or more from the edge of the traveled way, the height to the bottom of such signs may be 1.5 m (5 ft) above the level of the pavement edge.
A route sign assembly consisting of a route sign and auxiliary signs (see Section 2D.27) may be treated as a single sign for the purposes of this Section.
The mounting height may be adjusted when supports are located near the edge of the right-of-way on a steep backslope.
Support:
Without this flexibility regarding steep backslopes, some agencies
might decide to relocate the sign closer to the road, which might
be less desirable.
Standard:
Overhead mounted signs shall provide a vertical clearance of not
less than 5.2 m (17 ft) to the sign, light fixture, or sign bridge,
over the entire width of the pavement and shoulders except where
a lesser vertical clearance is used for the design of other structures.
Option:
If the vertical clearance of other structures is less than 4.9 m
(16 ft), the vertical clearance to overhead sign structures or supports
may be as low as 0.3 m (1 ft) higher than the vertical clearance
of the other structures.
In special cases it may be necessary to reduce the clearance to overhead signs because of substandard dimensions in tunnels and other major structures such as double-deck bridges.
Support:
Figure 2A-1 illustrates some examples of
the mounting height requirements contained in this Section.
Section 2A.19 Lateral Offset
Standard:
For overhead sign supports, the minimum lateral offset from the
edge of the shoulder (or if no shoulder exists, from the edge of
the pavement) to the near edge of overhead sign supports (cantilever
or sign bridges) shall be 1.8 m (6 ft). Overhead sign supports shall
have a barrier or crash cushion to shield them if they are within
the clear zone.
Ground-mounted sign supports shall be breakaway, yielding, or shielded with a longitudinal barrier or crash cushion if within the clear zone.
Guidance:
For ground-mounted signs, the minimum lateral offset should be 3.7
m (12 ft) from the edge of the traveled way. If a shoulder wider
than 1.8 m (6 ft) exists, the minimum lateral offset for ground-mounted
signs should be 1.8 m (6 ft) from the edge of the shoulder.
Support:
The minimum lateral offset is intended to keep trucks and cars that
use the shoulders from striking the signs or supports.
Guidance:
All supports should be located as far as practical from the edge
of the shoulder. Advantage should be taken to place signs behind
existing roadside barriers, on over-crossing structures, or other
locations that minimize the exposure of the traffic to sign supports.
Option:
Where permitted, signs may be placed on existing supports used for
other purposes, such as highway traffic signal supports, highway
lighting supports, and utility poles.
Standard:
If signs are placed on existing supports, they shall meet other
placement criteria contained in this Manual.
Option:
Lesser lateral offsets may be used on connecting roadways or ramps
at interchanges, but not less than 1.8 m (6 ft) from the edge of
the traveled way.
In areas where lateral offsets are limited, a minimum lateral offset of 0.6 m (2 ft) may be used.
A minimum offset of 0.3 m (1 ft) from the face of the curb may be used in urban areas where sidewalk width is limited or where existing poles are close to the curb.
Support:
Figures 2A-1 and 2A-2
illustrate some examples of the lateral offset requirements contained
in this Section.
Section 2A.20 Orientation
Guidance:
Unless otherwise stated in this Manual, signs should be vertically
mounted at right angles to the direction of, and facing, the traffic
that they are intended to serve.
Where mirror reflection from the sign face is encountered to such a degree as to reduce legibility, the sign should be turned slightly away from the road. Signs that are placed 9 m (30 ft) or more from the pavement edge should be turned toward the road. On curved alignments, the angle of placement should be determined by the direction of approaching traffic rather than by the roadway edge at the point where the sign is located.
Option:
On grades, sign faces may be tilted forward or back from the vertical
position to improve the viewing angle.
Section 2A.21 Posts and Mountings
Standard:
Sign posts, foundations, and mountings shall be so constructed as
to hold signs in a proper and permanent position, and to resist
swaying in the wind or displacement by vandalism.
Support:
The latest edition of AASHTO's "Specifications for Structural Supports
for Highway Signs, Luminaires, and Traffic Signals" contains additional
information regarding posts and mounting (see Addresses
for AASHTO's address).
Option:
Where engineering judgment indicates a need to draw attention to
the sign during nighttime conditions, a strip of retroreflective
material may be used on regulatory and warning sign supports.
Standard:
If a strip of retroreflective material is used on the sign support,
it shall be at least 50 mm (2 in) in width, it shall be placed for
the full length of the support from the sign to within 0.6 m (2
ft) above the edge of the roadway, and its color shall match the
background color of the sign, except that the color of the strip
for the YIELD and DO NOT ENTER signs shall be red.
Section 2A.22 Maintenance
Guidance:
Maintenance activities should consider proper position, cleanliness,
legibility, and daytime and nighttime visibility (see Section 2A.09).
Damaged or deteriorated signs should be replaced.
To assure adequate maintenance, a schedule for inspecting (both day and night), cleaning, and replacing signs should be established. Employees of highway, law enforcement, and other public agencies whose duties require that they travel on the roadways should be encouraged to report any damaged, deteriorated, or obscured signs at the first opportunity.
Steps should be taken to see that weeds, trees, shrubbery, and construction, maintenance, and utility materials and equipment do not obscure the face of any sign.
A regular schedule of replacement of lighting elements for illuminated signs should be maintained.
Section 2A.23 Median Opening Treatments for Divided Highways with Wide Medians
Guidance:
Where divided highways are separated by median widths at the median
opening itself of 9 m (30 ft) or more, median openings should be
signed as two separate intersections.
